Did you know that nearly 1 in 8 men will be diagnosed with prostate cancer during their lifetime? This fact underlines the need to grasp Prostate Cancer Grading. It’s vital for figuring out how serious the cancer is and what treatments might work best. The Gleason Score checks cancer cells under a microscope to rate their aggression, with scores from 6 to 10. A higher score means the cancer may be more aggressive, guiding doctors in treatment planning.
Grade Groups make it simpler to classify the cancer’s severity into five levels. This helps patients and doctors understand the cancer’s aggression more clearly. This system helps in determining how the disease might progress and in creating personalized treatment strategies. For more details on the Gleason Score and Grade Groups, you can check out this helpful resource.
Key Takeaways
- The Gleason Score ranges from 6 to 10 and is pivotal in determining cancer’s aggressiveness.
- Grade Groups offer a simplified grading system ranging from 1 (least aggressive) to 5 (most aggressive).
- Understanding these grading systems helps guide treatment decisions based on individual patient circumstances.
- Prostate cancer’s biological behavior is categorized into low, intermediate, and high-risk groups based on various factors.
- Keeping informed about grading can empower patients to engage meaningfully in treatment discussions with their healthcare providers.
Understanding Prostate Cancer and Its Impact
Prostate cancer is the top cancer among men in the United States. It deeply affects their health and life quality. Despite often growing slowly, it can sometimes become aggressive and cause serious problems. Recognizing its impact on those affected and their families is crucial. It shows why we need more awareness and early screening.
Several factors, like age, family history, and lifestyle, can affect prostate cancer risk. Knowing these factors helps individuals talk about risks with doctors. Early diagnosis is key. It makes a big difference in how the cancer is treated and the possible outcomes.
Knowing the stages of prostate cancer is essential. The AJCC TNM system looks at tumor size, lymph node status, metastasis, PSA levels, and Gleason scores. This helps determine cancer’s severity. And, it guides doctors in choosing the best treatment options.
Here’s a quick guide to prostate cancer stages:
| Stage | Grade Group | PSA Level | Characteristics |
|---|---|---|---|
| I | 1 | Less than 10 | Localized cancer, minimal risk |
| IIA | 1 | 10-20 | Localized, possible higher risk |
| IIB | 2, 3, or 4 | Less than 20 | Localized but potentially more aggressive |
| III | 1 to 4 | At least 20 | Spread beyond prostate, more serious |
| IV | Any | Any | Metastatic cancer or nearby lymph node involvement |
The survival outlook varies by prostate cancer stage. From stages I to IVA, the survival is near 100%. This means men diagnosed early often live as long as those without cancer. However, for Stage IVB, survival falls to about 30%. This stage is more advanced and harder to treat.
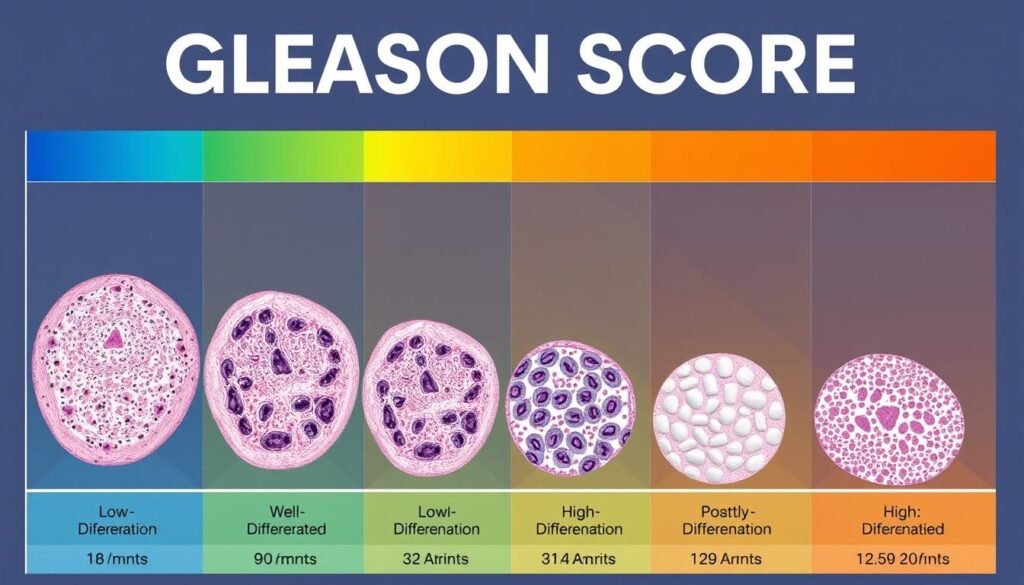
What is the Gleason Score?
The Gleason Score helps grade prostate cancer. It tells us how aggressive the cancer is. It was developed in the 1960s. This score looks at cancer cells under a microscope. It is crucial for diagnosing cancer.
History of the Gleason Score
Dr. Donald Gleason made this system to classify prostate cancer. It ranges from a score of 1 to 5. A score of 1 means cells look close to normal. But a score of 5 means the cells are very abnormal. This shows how important the Gleason Score is for prostate cancer evaluation.
How the Gleason Score is Determined
A pathologist looks at biopsy samples to find the Gleason Score. They add the two most common cell grades together. This gives a score between 2 and 10. Scores usually range from 6 to 10. They fit into specific Grade Groups, shown in the table below.
| Grade Group | Gleason Score | Description |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | 6 or lower | Low-grade cancer |
| 2 | 3 + 4 = 7 | Medium-grade cancer |
| 3 | 4 + 3 = 7 | Medium-grade cancer |
| 4 | 8 | High-grade cancer |
| 5 | 9 to 10 | High-grade cancer |
Higher scores mean the cancer grows faster and might spread. Scores of 6 and 7 are the most common. Knowing the Gleason Score helps decide on treatment. It makes a big difference in patient care. For more info on the Gleason grading system, click here.
Prostate Cancer Grading: The Gleason Score and Grade Groups
Understanding the grading of prostate cancer is crucial. The Gleason Score is a key tool in this process, with scores ranging from 2 to 10. Scores below 6 are rare and usually mean the cancer is not aggressive. The Grade Group system, introduced in 2014, helps make classification clearer.
Comparison Between Gleason Score and Grade Groups
The Gleason Score sorts prostate cancers into three groups:
- Low-grade: 6 or less
- Intermediate-grade: 7
- High-grade: 8 to 10
The Grade Group system breaks these down into five distinct groups:
- Grade Group 1: Gleason score 6 or less
- Grade Group 2: Gleason 3 + 4 = 7
- Grade Group 3: Gleason 4 + 3 = 7
- Grade Group 4: Gleason 8
- Grade Group 5: Gleason 9 or 10
This system helps doctors predict how the cancer will act and plan the best treatment. A Gleason score of 7 can mean different things based on the cancer’s makeup. Considering how much Grade 4 tissue is present helps in making accurate forecasts.
Getting prostate cancer grading right is vital for patient care. Both the Gleason Score and Grade Groups play key roles in choosing the right treatment.
Importance of Tumor Staging in Prostate Cancer
Tumor staging is key in understanding prostate cancer’s progression and seriousness. The TNM system helps gauge the disease’s extent. It looks at Tumor size (T), Node involvement (N), and Metastasis (M). This knowledge is vital for doctors to choose the best treatment options.
TNM Staging and Its Role
The TNM system is detailed as follows:
| Components | Classification | Description |
|---|---|---|
| T | T1 to T4 | Shows the tumor’s size and how far it’s spread in the prostate and nearby areas. |
| N | N0, N1 | N0 means the cancer hasn’t spread to nearby lymph nodes; N1 means it has. |
| M | M0, M1 | M0 indicates no distant metastasis; M1 shows cancer has spread to distant sites. |
Assessing these staging factors is crucial for the medical team. They use it to plan the right treatment. They consider things like the Grade Group, PSA levels, and biopsy results to tailor treatments. To learn more about surgery and what to expect, see this article.
Biopsy Results and Their Interpretation
Biopsies are key in diagnosing cancer, especially prostate cancer. They let doctors look closely at tissue samples. This helps them see if cancer is present and how aggressive it is. The process is crucial for determining the Gleason score. This score plays a big part in choosing the best treatment and affects patient outcomes.
How Biopsy Samples are Analyzed
In a prostate biopsy, usually 12 or more core samples are taken. These are from different parts of the prostate. The samples are then seen under a microscope by a pathologist. They check the cells’ looks and structure.
The Gleason score, ranging from 2 to 10, shows how aggressive the cancer is. Scores of 8 to 10 mean the cells look very abnormal. Scores under 6 suggest the cancer might not be as aggressive. This helps doctors put prostate cancer into categories. Well-differentiated cells have scores of 6 or less. Scores of 7 are for intermediate-grade cells. Poorly differentiated cells have scores of 8 to 10.
What to Expect from Your Biopsy Results
When you get biopsy results, you’ll learn about your Gleason score and Grade Groups. A score of 6 is usually good news. It means the cancer tends to grow slowly and is not very aggressive. But a score of 7 shows there’s a chance for more aggressive cancer. The primary and secondary grades tell doctors how fast it might grow.
These results are very important. They help decide the next steps for treatment. This might include hormone therapy to control the cancer’s growth. For more info on hormone therapy, check out this link.
Understanding Prognostic Factors in Prostate Cancer
Prognostic factors are very important in understanding what men diagnosed with prostate cancer can expect. Every year, more than 240,000 men in the U.S. are told they have prostate cancer. Most of these cases are found early. Knowing things like the Gleason Score, cancer stage, age, and health is key. It helps doctors decide on the best treatment and can predict survival chances.
Men with lower Gleason Scores usually do better than those with scores of 7 or above. For example, Gleason 6 tumors are linked to a very low chance of dying from this cancer. On the other hand, men with Gleason 4+3 tumors are three times more likely to die than those with Gleason 3+4. This shows how crucial it is to understand Gleason grades well.
The stage of cancer at diagnosis matters a lot too. People found with early-stage prostate cancer have a brighter outlook than those with later stages. Tools like the D’Amico Risk Classification help doctors figure out the risk of cancer returning after treatment. Other tools, like nomograms, use lots of factors to predict outcomes. They look at PSA levels, biopsy results, and age.
Sometimes, cancer spreading to nerves predicts a worse outcome, seen in 10% to 40% of cases. High PSA levels and other factors also make predictions tougher. Things like smoking and certain blood tests add to the complexity of outcomes. This shows why a broad approach is needed for accurate predictions.
Knowing about these prognostic factors helps doctors plan better treatments. It also makes patients more aware of their situation. As research and personalized medicine keep improving, our predictions will get better. This will help a lot in managing prostate cancer.
PSA Levels and Their Significance
Understanding PSA levels is crucial for diagnosing prostate cancer effectively. This test, focused on prostate-specific antigen, identifies and monitors prostate health. High PSA levels could mean various conditions, with prostate cancer as a main worry. We will explore PSA’s role in cancer diagnosis and how it affects treatment choices.
Role of PSA in Prostate Cancer Diagnosis
The FDA first approved the prostate-specific antigen test in 1986. It was for monitoring prostate cancer patients. By 1994, the test also helped in early detection for men over 50. A PSA level under 4.0 ng/mL was considered normal back then. Yet, factors like age can change these results.
About 25% of men with high PSA levels need a biopsy, and some are found to have cancer. This shows the test’s limits and the chance of false positives.
PSA Levels and Treatment Decisions
PSA levels are crucial in deciding on treatment. For men with levels between 4 and 10, the cancer risk is about 25%. Levels above 10 raise the chance to over 50%. Even men with lower levels can have cancer, showing the need for more tests or close watching.
Risk factors like age, family history, and other conditions like benign prostatic hyperplasia can make PSA results tricky to interpret. Depending on the PSA level and other diagnostic info like the Gleason Score, treatment options can vary a lot. Thus, knowing the PSA level accurately is key to choosing the best treatment approach.
| PSA Level (ng/mL) | Risk of Prostate Cancer | Recommended Action |
|---|---|---|
| Below 4.0 | Low | Routine Monitoring |
| 4.0 – 10.0 | 25% Chance | Consider Biopsy |
| Above 10.0 | Over 50% Chance | Immediate Evaluation |
In short, PSA levels are key in diagnosing and planning treatment for prostate cancer. They are important not just for initial screening, but for managing prostate health overall.
Treatment Options Based on Gleason Score and Grade Groups
How we treat prostate cancer depends a lot on the tumor’s Gleason Score and Grade Groups. These help us pick the best treatment plan for each person. We can use surgery, radiotherapy, or keep a close watch, based on how severe the cancer is.
Surgical Options
Many people with prostate cancer have surgery. Taking out the prostate gland and nearby tissues is a common method. This is important for those at a medium or higher risk when cancer hasn’t spread outside the prostate. Surgery works best when combined with other treatments like hormone therapy or radiation in tougher cases.
Radiotherapy and Hormone Therapy
Radiotherapy comes in different types, like external radiation or brachytherapy. People with high-risk prostate cancer often get radiotherapy with hormone therapy. This mix helps slow down the cancer and makes the treatment work better. In advanced Stage IV B, treatments might include hormone therapy with new drugs or chemotherapy, aiming for a full-fledged attack on the cancer.
Active Surveillance Strategies
If the cancer is very low or low-risk, active surveillance might be the best choice. It means keeping an eye on the cancer with regular tests and biopsies, without rushing into treatment. This approach helps avoid too much treatment for cancers that might not grow fast or spread.
Precision Medicine in Prostate Cancer
Precision medicine is vital in prostate cancer, focusing on care for each patient’s unique needs. It uses factors like genetic markers and tumor profiles to customize treatments. Advanced techniques, such as copy number alterations (CNAs) analysis, help doctors understand tumor behavior. This leads to better treatment plans.
A six-gene CNA classifier looks promising for those with low or intermediate risk. While some genes like RB1 and CHD1 didn’t predict outcomes well, loss of RWDD3 and WRN links to recurrence and genomic instability. This knowledge helps create more personalized treatments, reducing unnecessary therapies and improving management.
The growth of precision medicine in prostate cancer has seen hurdles. Yet, research on genome profiling and gene fusions is improving outcomes. Efforts to mix health data with standard cancer grading and staging are guiding better treatment choices.
In conclusion, precision medicine marks a leap forward in caring for prostate cancer. It aims for improved outcomes with targeted therapies. As research continues, patient care will inevitably advance.
Conclusion
Grasping prostate cancer grades, especially the Gleason Score and Grade Groups, is key for patients and doctors. It sheds light on cancer traits, how it might progress, and the best treatment to choose. It’s crucial since under half of the patients really get the terms used in their diagnosis.
Since 2005, and again in 2014, the Gleason grading system has been refined. This was to better align tumor grades seen in needle biopsies with those from complete prostate removals. Such refinements help in predicting outcomes better. For instance, a higher Gleason score means a higher risk, highlighting why correct grading is necessary for picking the right treatment.
Understanding these grades well helps in making key decisions like whether to watch and wait, go for surgery, or opt for radiotherapy. As medical science advances, keeping these grades in mind is essential for top-notch patient care and results.