It’s shocking to know that about half of the people with local prostate cancer will face metastatic cancer. This fact highlights the need to grasp what metastatic prostate cancer is all about. It’s when cancer cells move beyond the prostate to other body parts. Although it can’t be cured, it’s key to understand that effective management allows those with advanced prostate cancer to live well for years. Treatment options include hormone therapies, chemotherapy, radiation, and sometimes surgery. These treatments help manage symptoms and improve life quality.
Grasping how metastatic prostate cancer works is vital for both patients and caregivers. It helps them understand what treatment options are available and what to expect in terms of prognosis. Through knowledge of different stages and treatment methodologies, health professionals can design specific treatment plans. These plans aim to extend life and enhance the well-being of those living with this diagnosis.
Key Takeaways
- About 50% of localized prostate cancer cases may develop into metastatic cancer later in life.
- Metastatic prostate cancer can significantly affect the quality of life, but many manage to live normally for years.
- Various treatment options, including hormone therapy and chemotherapy, play a critical role in managing advanced prostate cancer.
- Prostate-specific antigen (PSA) screening has drastically reduced the diagnoses of metastatic prostate cancer.
- The importance of a personalized treatment approach can increase survival rates for individuals diagnosed with metastatic prostate cancer.
Understanding Prostate Cancer and Its Progression
Prostate cancer is a major health issue for many men, especially as they get older. Knowing about it and how it can progress is key for handling and treatment. The prostate gland is under the bladder and is important for male reproductive health. Most prostate cancers start from a type called adenocarcinomas. Age, family history, and ethnicity can increase the risk of getting this disease.
The Basics of Prostate Cancer
Prostate cancer begins in the prostate gland. It often grows slowly, but sometimes it can be fast. Many men don’t know they have it early on because it doesn’t cause symptoms straight away. Checking PSA levels is important for spotting prostate cancer early. High PSA levels might mean cancer, but it’s not always sure.
What Happens When Prostate Cancer Spreads?
Advanced prostate cancer can spread, first to lymph nodes close by. Then, it may go to the bones, lungs, liver, or even the brain. Over 60% of men with late-stage prostate cancer will have it spread to their bones. Only about 34% of these men will live for five years after the cancer spreads widely.
To fight cancer spread, understanding how it moves is crucial. Treatments like Zometa help keep bones healthy and prevent breaks. People with cancer just in some bones often do better than those with cancer all over.
Staging of Prostate Cancer and Metastasis
It’s important to understand the stages of prostate cancer. This knowledge helps judge how far the disease has spread. Knowing the stage helps doctors decide on the best treatment. Advanced prostate cancer means the cancer has grown a lot. It may affect nearby parts, lymph nodes, or organs far away.
What is Advanced Prostate Cancer?
Advanced prostate cancer is when the cancer spreads from the prostate. It usually means Stage IV cancer, affecting distant organs or tissues, like bones. Doctors use this information to plan the right treatment. The AJCC TNM system checks tumor size, lymph node spread, and distant metastasis to find the stage.
Understanding Stage IV Prostate Cancer
Stage IV, or metastatic prostate cancer, divides into Stage IVA and IVB. Stage IVA involves local spread. Stage IVB means the cancer has spread to far organs. The cancer is classified by T, N, and M stages. Treatment options can be very different, depending on the cancer’s details.
| Stage | T (Tumor Size) | N (Lymph Node Involvement) | M (Metastasis) | Gleason Score | PSA Level |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Stage I | cT1 | N0 | M0 | Grade Group 1 (6 or less) | <10 |
| Stage II | T1 or T2 | N0 | M0 | Grade Group 2 (3+4=7) | <20 |
| Stage III | T1 or T2 | N0 | M0 | Grade Group 1-4 (8 or less) | >=20 |
| Stage IV | Any T | Any N | M1 | Any Grade Group | Any PSA |
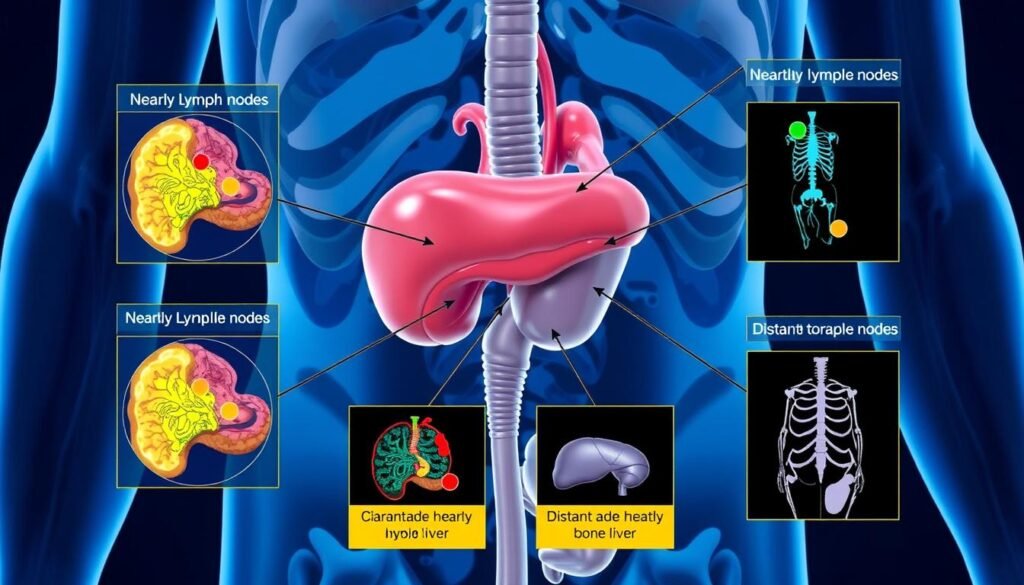
How Does Metastatic Prostate Cancer Spread?
It’s important to know how metastatic prostate cancer spreads for good treatment. This cancer mainly travels through two ways: the lymphatic system and the bloodstream. It often first spreads to nearby lymph nodes. These nodes play a big role in our body’s defense and transport lymphatic fluid.
Common Sites for Metastasis
Prostate cancer often spreads to certain places in the body. Studies show that bones are the most common spot, making up 85% to 90% of all prostate cancer metastases. Other areas where it can spread include:
- Liver
- Lungs
- Brain
While most metastases happen in bones, cancer can also go to the liver, lungs, and brain. This makes treatment harder and the outlook worse. About 16% of men with new prostate cancer diagnoses already have distant metastases. This greatly affects their survival chances.
Mechanisms of Cancer Spread: Lymphatic and Blood Systems
Metastatic prostate cancer spreads through the lymphatic system and the bloodstream. The cancer invades lymphatic vessels to get to nearby lymph nodes. From there, it can move to the bloodstream. This lets the cancer reach far-off places in the body. About 5-7% of men will have metastatic prostate cancer when they’re first diagnosed. This shows how crucial early detection and ongoing checks are.
Knowing how the cancer spreads helps with early diagnosis and planning treatment. This can lead to better results for patients.
Symptoms and Diagnosis of Metastatic Prostate Cancer
Finding out the signs of advanced disease helps in starting treatment early. Men with metastatic prostate cancer may face many symptoms. These can really affect how they feel every day. Knowing these signs early leads to better Diagnosis and care.
Identifying Symptoms of Advanced Disease
Advanced prostate cancer often spreads to other parts of the body. This can cause certain symptoms. The bones are the most common place it spreads to. Patients might feel ongoing bone pain. This pain usually means the cancer has spread. Weaker bones also might break more easily.
When cancer spreads to the lymph nodes, swelling and discomfort can happen. If the liver is affected, one might have stomach pain, feel sick, lose weight, and turn yellow. Lung spread could cause lasting coughs, trouble breathing, and sometimes coughing up blood. This shows how key regular checks are.
Urinary problems can include needing to go quickly, pain when peeing, and blood in the urine. If the bowel gets involved, it might lead to not being able to go, stomach pain, and bleeding from the back. All these symptoms can make life hard, showing how crucial symptom control teams are.
Blood tests are very important for finding metastatic prostate cancer. Checking levels of a specific marker in the blood can show if the cancer is getting worse. Knowing how these levels change helps doctors decide on the best treatment.
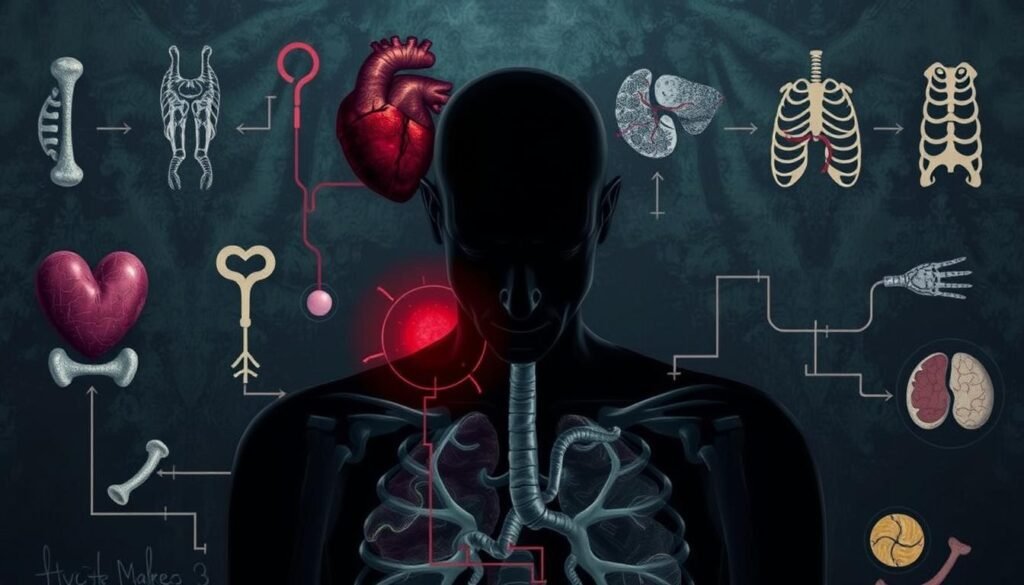
Advanced prostate cancer can’t be cured, but it can be treated. The aim is to manage symptoms and make life better. This highlights the value of spotting it early and starting treatment right away.
Prostate Cancer Treatment Options
Treating prostate cancer that has spread involves different methods. These methods focus on the patient’s needs. Hormone therapy, chemotherapy, radiation, and new treatments are used. The choice of treatment looks at how far the cancer has spread, the patient’s health, and personal treatment preferences.
Overview of Treatment Modalities
Various methods are available for treating advanced prostate cancer. Each one aims to reduce symptoms, slow the cancer’s growth, and may help patients live longer. The most common treatments include:
- Hormone therapy – This therapy reduces testosterone to slow or shrink cancer.
- Surgery – Removing the testicles decreases testosterone and helps with symptoms.
- Radiation therapy – Targets cancer cells and can ease pain in advanced cases.
- Chemotherapy – Often used for stage 4 prostate cancer, it helps slow growth and eases symptoms.
- Targeted drug therapy and immunotherapy – Used when other treatments don’t work, they target cancer cells directly.
- Palliative care – Focuses on improving life quality and managing symptoms without curing the disease.
Importance of a Multimodal Treatment Approach
A multimodal approach is key for treating advanced prostate cancer. It combines different therapies to fight the cancer more effectively and improve the patient’s quality of life. Clinical trials are important. They help find new treatments for advanced prostate cancer, giving patients access to the latest options.

Hormone Therapy in Managing Metastatic Prostate Cancer
Hormone therapy is key in treating metastatic prostate cancer. It mainly uses androgen deprivation therapy (ADT) to work. ADT lowers androgens like testosterone, which helps prostate cancer cells grow. By reducing these hormones, the therapy can slow the cancer’s progress. It also helps improve patients’ lives.
Androgen Deprivation Therapy Explained
ADT can be done in various ways, including:
- Surgical castration via orchiectomy, which cuts testosterone levels by 90% to 95%.
- LHRH agonists such as Leuprolide and Goserelin that stop the release of luteinizing hormone. This reduces androgen production.
- LHRH antagonists like Degarelix, which block luteinizing hormone release without causing an initial testosterone surge.
- Androgen receptor blockers including drugs such as flutamide, bicalutamide, and enzalutamide. They prevent androgens from signaling cancer cell growth.
- Androgen synthesis inhibitors like abiraterone that block necessary enzyme activity for androgen production.
Choosing hormone therapy involves picking the best treatment mix. The goal is to be as effective as possible while limiting side effects.
Benefits and Risks of Hormone Therapy
Hormone therapy brings significant benefits in controlling metastatic prostate cancer. It can make tumors smaller, slow their growth, and lessen pain. However, it has risks. Side effects include:
- Loss of muscle mass
- More body fat
- Lower sex drive and erectile dysfunction
- Hot flashes
- Thinner bones
- Risk of heart problems
To manage side effects, doctors may suggest periodic hormone therapy. They also monitor patients closely. This helps balance treatment success with side effect management.
Chemotherapy for Advanced Prostate Cancer
Chemotherapy is key in treating advanced prostate cancer, mainly when hormone therapy fails or symptoms appear. It’s not the go-to for early-stage cancer but is critical as the disease advances.
When is Chemotherapy Recommended?
Doctors suggest chemotherapy for advanced prostate cancer that has spread beyond the prostate. Docetaxel, combined with steroids like prednisone, is usually tried first. If docetaxel doesn’t work well, cabazitaxel might be next. This strategy aims to boost survival rates. Though it doesn’t cure cancer, chemotherapy can reduce tumors, slow their growth, ease symptoms, and better life quality.
Potential Side Effects of Chemotherapy
Chemotherapy comes with side effects, which can vary. Common ones include:
- Nausea
- Fatigue
- Hair loss
- Mouth sores
- Loss of appetite
- Diarrhea or constipation
- Increased risk of infections
Sometimes, chemotherapy may cause severe allergic reactions or even nerve damage. In rare cases, long-term issues like leukemia could arise from certain drugs. It’s crucial for patients to talk openly with their doctors about any side effects. They should also mention any other treatments they’re trying, as they could interfere with the chemotherapy.
Treatment cycles typically span three weeks. Before each cycle, blood tests are done to ensure patient safety. Treatments might be given through IV at a healthcare facility or at home with portable pumps, depending on the situation.
Emerging Treatments: Immunotherapy and Targeted Therapies
Recent advances in metastatic prostate cancer treatment have brought in new methods. These include immunotherapy and targeted therapies. They aim to improve how well treatments work and the health outcomes for patients. This is especially true when standard treatments might not be enough.
Understanding Immunotherapy Options
Immunotherapy is a cutting-edge method. It uses our immune system to fight off cancer cells. For example, sipuleucel-T, an approved treatment, boosts the immune system to attack prostate cancer. In one study, the Phase 1b KEYNOTE-028 trial, about 17% of patients saw their cancer respond to this treatment. This shows the promise of immunotherapy but also why we must keep researching and refining these treatments.
What are Targeted Therapies?
Targeted therapies aim at specific parts of cancer cells. This makes the treatment more specific. Drugs like Rucaparib, Olaparib, and Talazoparib are effective against certain prostate cancers. They work well when the cancer has specific genetic markers, like changes in the BRCA gene. Patients must be monitored for side effects like nausea and tiredness. They also need genetic tests before starting these treatments.
The way we treat prostate cancer is changing with these new treatments. Ongoing research is key to understanding how best to use them. They have the potential to significantly improve outcomes for patients. For more on managing prostate symptoms, click here.
Palliative Care and Quality of Life Considerations
Palliative care is key in treating advanced prostate cancer. It’s not just about the end of life. It also aims to improve life quality for those with tough symptoms. Palliative care teams work to ease physical pain, emotional upset, and spiritual worries tied to cancer.
The Role of Palliative Care in Advanced Prostate Cancer
Palliative care experts work closely with patients. They aim to manage symptoms and boost life quality. They help with issues from treatments or the cancer itself, like:
- Frequent urination and difficulty during the process
- Bone pain and fatigue from hormone or radiation therapy
- Emotional struggles with loss of sexual drive and incontinence
Good communication with palliative care teams aids in decision-making. Palliative care pros help discuss both medical and emotional needs.
Managing Symptoms and Improving Quality of Life
Effectively managing symptoms can greatly enhance life quality for men with advanced prostate cancer. Palliative care uses many strategies, including:
| Symptom | Management Strategy | Additional Support |
|---|---|---|
| Pain | Use of appropriate pain medications, including steroids | Counseling about pain management techniques |
| Fatigue | Medication adjustments and lifestyle changes | Energy management through physical activities |
| Emotional distress | Family discussions to address anxiety and reinforce support | Access to counseling services |
| Communication with providers | Clarity in discussing treatment goals and options | Regular check-ins with healthcare teams |
About 30% of men will face metastases, deeply affecting life quality. Recognizing symptoms like bone pain and mental struggles is crucial. Palliative care is all about giving full support, letting patients face their diagnosis with dignity and less pain.
Conclusion
Metastatic prostate cancer is a big challenge for both patients and healthcare providers. In 2022, about 268,490 new cases were diagnosed in the U.S. Understanding this disease is key to managing it well. Treatments like hormone therapy and chemotherapy help a lot. They can lift survival rates significantly.
Androgen deprivation therapy with docetaxel shows promise. It can extend life to 59.1 months for advanced cases. This gives hope.
New treatments like abiraterone acetate and immunotherapy are changing the game. But, the focus on research continues to refine these treatments. A team approach helps manage symptoms. This ensures a better life for patients despite the challenges. Educational resources and trials help patients choose their treatment wisely.
Even with the complexity of metastatic prostate cancer, progress in treatment offers better health chances. The aim is to manage the disease well while keeping a good life quality. Ongoing research and new therapies are key. For more on the implications of screening and treatment, this study sheds light on PSA’s potential benefits and harms.