Did you know that 1 in 8 men will face prostate cancer in their lives? This fact underscores the importance of knowing the best early treatment options. When caught early, the cancer hasn’t spread far, offering more treatment choices. Today, patients benefit from advanced treatments and monitoring, leading to customized care that balances effectiveness with life quality.
Talking about screening is crucial, especially for men over 50 or with a family history of prostate cancer. Adopting a healthy lifestyle can also help fend off prostate cancer. This includes daily exercise and a diet low in sugar. Knowing your treatment options early on is key to making smart decisions. We’re digging into the options available for men at this pivotal time.
Key Takeaways
- 1 in 8 men will be diagnosed with prostate cancer.
- Early stage treatment often includes active surveillance for low-risk cases.
- Healthy lifestyle choices can reduce risk and improve outcomes.
- Biopsy procedures have no reported incidents of spreading prostate cancer.
- The Gleason score helps predict cancer aggressiveness and treatment pathways.
- Personalized treatment strategies are becoming increasingly available.
Understanding Early Stage Prostate Cancer
Early-stage prostate cancer is found at stages I or II. This means it hasn’t spread outside the prostate gland. Most cases are caught when the cancer is still local. Knowing about this is key to fighting the disease.
Early-stage prostate cancer grows slowly. This allows for treatments that fit individual needs. Doctors give advice using prostate cancer treatment guidelines. These cover many treatment options.
Three main treatments are: active surveillance, surgery, and radiation therapy. Active surveillance means watching the cancer closely. Doctors use PSA blood tests and biopsies every few months to keep an eye on it.
Surgery, like radical prostatectomy, removes the prostate and some nearby tissue. Techniques such as retropubic or perineal prostatectomy may be used. Which one depends on the patient’s health and what they prefer.
Radiation therapy is another common choice. It uses high-energy X-rays or radioactive pellets to fight cancer. But, it can cause problems like diarrhea, trouble controlling urine, and tiredness.
Other options include cryosurgery and hormone therapy. These work in different ways to attack cancer cells. Hormone therapy slows cancer by affecting male hormones. Side effects can include trouble with erections and bladder issues.
Making a treatment choice is tough. Men with early prostate cancer should think about their age and health. While no treatment is best for everyone, getting advice from different doctors helps. They provide more info on treatment choices.
| Treatment Option | Description | Potential Side Effects |
|---|---|---|
| Active Surveillance | Regular monitoring of cancer without immediate treatment. | Minimal, but anxiety over the diagnosis may arise. |
| Surgery | Removal of the prostate and some surrounding tissue. | Bladder control issues, erectile dysfunction, and fertility concerns. |
| Radiation Therapy | External or internal radiation targeting cancer cells. | Diarrhea, urinary incontinence, erectile dysfunction, fatigue. |
| Cryosurgery | Freezing cancer cells to kill them. | Bladder issues, erectile dysfunction. |
| Hormone Therapy | Inhibits male hormone action to slow cancer growth. | Decreased sex drive, bone thinning, and potential erectile dysfunction. |
Prostate Cancer Staging and Risk Groups
Doctors use the TNM system to stage prostate cancer. It looks at the tumor size, if it has spread to lymph nodes, and if there’s distant metastasis. Understanding the PSA level and Gleason score is the first step. These measures tell how aggressive the cancer is.
Prostate cancer stages go from I to IV. Stage I means the tumor can’t be felt or seen in scans, and it has a low Gleason score and PSA level. Stages IIA to IIC show the tumor’s size and if lymph nodes are involved. This helps in understanding the cancer’s growth.
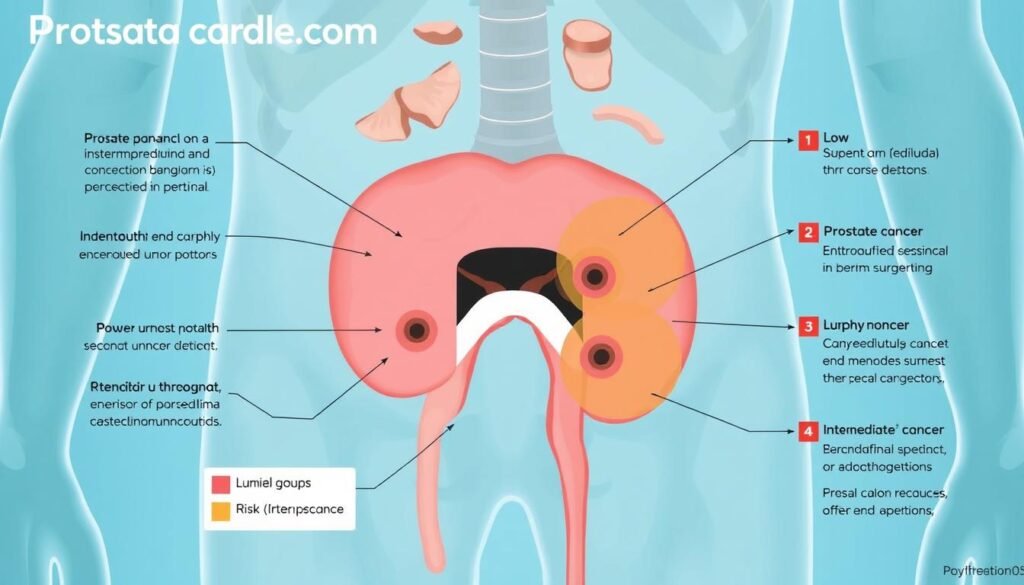
Stages III and IV indicate a higher risk due to changes in PSA levels and Gleason score. Stage III cancer has grown outside the prostate but hasn’t spread to lymph nodes or distant areas. Stage IV means the cancer has spread to lymph nodes or other organs. Choices about treatment depend greatly on these stages.
Risk groups help decide on the best treatment plan. They divide patients into low, intermediate, and high risk. This is based on their Gleason score and PSA levels. Low-risk patients might just watch and wait. But, high-risk patients could need surgery or radiation. Knowing the risk group helps tailor the treatment to each patient, aiming for the best results.
| Stage | T Category | N Category | M Category | Gleason Score |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| I | T1-T2a | N0 | M0 | 6 or less |
| IIA | T2b | N0 | M0 | 7 |
| IIB | T2c | N0 | M0 | 7 |
| IIC | T2c | N0 | M0 | 8-10 |
| III | T3a-T4 | N0 | M0 | 8-10 |
| IV | Tany | N1 | M1 | Varies |
Deciding on Treatment Options
Upon hearing you have prostate cancer, knowing your options is key. You’ll need to talk in-depth with your healthcare team. They’ll help you pick a treatment that’s right for you, considering your age, health, and the cancer’s risk of getting worse.
There are many ways to deal with prostate cancer. Choices range from watching it closely to going in for surgery or radiation. Each option affects how urgent the treatment is, how well it might work, and what side effects there might be.
Surgery is a top choice for many. It’s often done with robots and is less harsh than traditional methods. This makes recovery easier and cuts down on side effects. Radiation therapy, like blasting the cancer with a beam or placing radioactive seeds, is also a main way to treat it.
People with advanced cancer might need hormone therapy. Chemo is usually for those at high risk or if the cancer has spread. What’s best for you depends on the specifics of your cancer. Custom plans often lead to the best results.
As experts advise, think about how treatments will affect your life. Making a well-thought-out choice helps you take charge of your prostate cancer treatment path. By looking at the good and bad, you’ll be able to make smarter decisions.
| Treatment Option | Ideal Candidate | Potential Side Effects |
|---|---|---|
| Surgery (Radical Prostatectomy) | Localized cancer without spread | Urinary incontinence, erectile dysfunction |
| Radiation Therapy | Localized tumors, some metastatic cases | Fatigue, urinary issues, impotence |
| Hormone Therapy | Advanced cancer, Gleason score 8+ | Hot flashes, weight gain, fatigue |
| Chemotherapy | High-risk or recurrent cancer | Nausea, fatigue, increased infection risk |
| Cryotherapy | Localized cancer, surgery not viable | Pain, urinary changes |
Best Treatment for Prostate Cancer in Early Stages
When looking for the best treatment for prostate cancer in its early stages, there are many options. These options are designed to fit each person’s unique needs. Early-stage prostate cancer can be managed in different ways, each with its own benefits.
Active Surveillance and Watchful Waiting
Active surveillance is for men with low-risk prostate cancer. It means watching the cancer closely instead of treating it right away. This method helps avoid treatments that aren’t needed yet. Patients go through regular PSA tests, MRI scans, and biopsies to monitor the cancer.
In contrast, watchful waiting is better for older men or those without symptoms. Treatment is delayed until necessary. This method shows how prostate cancer care has improved, focusing on what’s best for the patient.
Surgery Options: Radical Prostatectomy
Radical prostatectomy removes the prostate gland and some tissues around it. It’s for patients whose cancer hasn’t spread. Robotic-assisted surgery may help patients recover faster and with fewer issues. However, risks like urinary problems and erectile dysfunction exist. People must discuss these with doctors before deciding.
Radiation Therapy Techniques
Radiation therapy is key for treating prostate cancer that hasn’t spread far. Techniques like IMRT, SBRT, and Brachytherapy help doctors create customized plans. Brachytherapy, or radioactive seed placement, focuses on balancing success and risks. Adding hormone therapy might also block cancer growth. For more information, check out radiation therapy recommendations.
| Treatment Option | Description | Potential Side Effects |
|---|---|---|
| Active Surveillance | Regular monitoring without immediate treatment | None, but anxiety about monitoring |
| Radical Prostatectomy | Surgical removal of the prostate gland | Urinary incontinence, erectile dysfunction |
| Radiation Therapy | External or internal radiation to kill cancer cells | Fatigue, urinary problems, rectal irritation |
| Brachytherapy | Radioactive seeds implanted in the prostate | Urinary problems, lower risk of sexual dysfunction |
Emerging Treatment Options and Breakthroughs
Medical research has brought new methods for treating prostate cancer. These new treatments are not just more effective. They also cause fewer side effects than old ones. This means better health and life quality for patients.
Focal Therapies and Their Benefits
Focal therapies are a big step forward in treating prostate cancer. They focus only on the tumor. This means fewer issues like incontinence and erectile dysfunction than with older treatments. They’re less invasive, so they’re good for patients who want to keep living well while fighting cancer.
High-Intensity Focused Ultrasound (HIFU)
High-Intensity Focused Ultrasound (HIFU) is a leading-edge method in the fight against prostate cancer. It uses focused sound waves to heat and kill cancer cells, being less invasive. This approach aims to better preserve urinary and sexual functions after treatment. It’s a promising move towards more effective treatments with less harm.
| Treatment Option | Invasiveness | Potential Side Effects | Effectiveness |
|---|---|---|---|
| Traditional Surgery | High | Incontinence, Erectile Dysfunction | High |
| Radiation Therapy | Medium | Fatigue, Urinary Issues | High |
| Focal Therapies | Low | Minimal | Promising |
| High-Intensity Focused Ultrasound (HIFU) | Low | Minimal | Promising |
Considerations for Choosing Treatment
Choosing the right prostate cancer treatment involves looking at many personal things. The tumor’s stage and grade are key, along with the patient’s age, health, and family cancer history. Genetic and biomarker testing also help decide the best action.
Active surveillance is a way to manage low-risk prostate cancer without rushing treatment. It includes regular PSA tests, rectal exams, and biopsies. Knowing the prostate cancer treatment success rate is crucial. This information helps patients make choices about side effects they are willing to face.
Urinary incontinence and erectile dysfunction are common side effects of prostate cancer treatments. It’s important each treatment choice matches the person’s health goals and how they want to live.
The National Cancer Institute recommends thinking about other health problems when choosing a treatment. For prostate cancer that hasn’t spread, surgery or prostatectomy might be best. Radiation therapy is also an option, used alone or with surgery or hormone therapy. Chemotherapy and hormone therapy are for more advanced stages.
Targeted therapy and immunotherapy are newer methods focusing on killing cancer cells while saving healthy ones. Tools like the Interactive Decision Support Tool help patients understand their options fully. It guides them to make informed decisions for their treatment.
| Factor | Consideration |
|---|---|
| Tumor Stage and Grade | Importance of treatment type and level of aggressiveness |
| Age | Impact on treatment choices and recovery |
| Overall Health | Presence of other health issues affecting treatment decisions |
| Family History | Potential inherited risks influencing treatment |
| Genetic Testing | Insights on cancer progression and treatment efficacy |
| Availability of Care | Access to specialized treatment facilities and professionals |
Understanding Treatment Side Effects
Every treatment for prostate cancer might lead to side effects that deeply affect a patient’s life. Understanding these side effects is crucial. It helps patients make informed decisions and manage the side effects better.
Short-Term and Long-Term Impact
Short-term and long-term side effects vary from one patient to another. Some common issues are:
- Erectile dysfunction, a common issue, may continue, impacting a man’s ability to father children.
- Urinary incontinence could affect daily activities, especially after surgery.
- Bowel problems might include diarrhea or bleeding, often due to radiation therapy.
- Temporary urinary symptoms can disrupt sleep with frequent night-time urination.
The stage of the cancer and Gleason score play key roles in the severity of side effects. They help guide the choice of treatment.
Managing Side Effects Effectively
There are effective ways to lessen the negative impact of side effects. Some strategies include:
- Medications that specifically target issues like incontinence and erectile dysfunction.
- Making lifestyle adjustments, such as physical therapy, can improve urinary control.
- Seeking supportive care offers emotional support through counseling and groups.
Patient consultation with healthcare experts is essential. It ensures that management plans are tailored to individual needs.
| Side Effect | Short-Term Impact | Long-Term Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Erectile Dysfunction | Difficulty achieving or maintaining an erection | Permanently affected sexual function |
| Urinary Incontinence | Increased frequency of urination | Potential for chronic incontinence |
| Bowel Problems | Temporary bowel irritation | Long-lasting bowel dysfunction |
| Fatigue | Feeling tired or exhausted regularly | Ongoing energy depletion and weakness |
Finding the Right Treatment Center
Choosing the right prostate cancer treatment center is very important. It shapes how treatment will go and the results for patients. It gives access to advanced technology and specialized knowledge in treating this cancer.
The Smilow Comprehensive Prostate Cancer Center uses a team approach. It includes urologic surgeons, radiation oncologists, and even naturopathic doctors. This teamwork leads to a treatment plan that’s just right for each patient. It covers medical and supportive therapies.
NYU Langone is a leader in national rankings. It’s tied for No. 2 in urology by U.S. News & World Report for 2024–25. The high skills of the doctors and strong support systems improve patient experiences and outcomes.
Having skilled surgeons and teams means better results and fewer problems. For radiation therapy patients, experienced teams mean improved outcomes. At places like Memorial Sloan Kettering, patients can try new treatments and tests. This leads to big advancements in treating prostate cancer.
When looking for a treatment center, individuals should:
- Look into the center’s treatments and special areas.
- Get recommendations from doctors they trust.
- Read what other patients say and look at the center’s success rates.
- Think about centers that treat the whole person, not just the cancer.
Going to a top prostate cancer treatment center helps a lot. It makes treatment work better and helps patients through their cancer journey. Patients should ask about new treatments and programs that focus on their health and happiness.
| Center Name | Accolade | Specialization |
|---|---|---|
| NYU Langone | Tied for No. 2 in Urology | Comprehensive Care |
| Smilow Comprehensive Prostate Cancer Center | Established in 2010 | Multidisciplinary Approach |
| Memorial Sloan Kettering | #1 in Urology Cancer Care | Access to Clinical Trials |
Conclusion
Understanding early-stage prostate cancer is key to improving patient outcomes. It often grows slowly, with many not knowing they have it until symptoms show. Spotting signs like urination issues or blood in urine is vital for early treatment.
Doctors use tests to figure out the cancer’s stage and plan the best treatment. This might mean watching the cancer, surgery, or radiation. Options like high-intensity focused ultrasound (HIFU) are also becoming popular.
Yet, it’s important to think about treatment side effects, such as erectile problems or urinary incontinence. Making choices means talking openly with your healthcare team and looking at all the info.
Each person’s experience with prostate cancer is different. With the right support and knowledge, patients can manage their treatment well. Focusing on early treatment and health can help improve life quality moving forward.